
In 2024, an era of extensive technology use, a consistent bombard of notifications, grind culture, and social media affect our nervous systems negatively. This requires effective tools to handle our mental health and overall well-being. Mastering Conscious breathing can be a game changer. Conscious breathing is not just a wellness trend but a strong tool ingrained in modern psychology and classical practices. In Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT), where feelings, thoughts, and behaviors are closely connected, conscious breathing provides a simple yet life-changing way to retrieve control over stress, anxiety, and negative thought patterns.
By employing the mind-body connection, conscious breathing soothes the nervous system, improves concentration, and sharpens emotional regulation. Many mental health professionals have recognized the power of conscious breathing in complementing CBT and modifying bad behaviors and thought patterns. So, stick with us till the end to learn how incorporating conscious breathing into CBT can boost its efficacy and offer long-lasting advantages for mental health.
The integration of conscious breathing into Cognitive Behavioral Therapy develops a powerful tool that handles not just mental health issues but emotional and physical ones too. The use of the mind-body connection in conscious breathing relaxes the nervous system, sharpens emotional regulation, and boosts concentration. Conscious breathing and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) together are the answer for ideal anxiety and stress management. Some of the powerful conscious breathing techniques are diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing, and Alternate nostril breathing. To get the most out of these breathing exercises, combine bobi _ a personal breathing device with conscious breathing exercises.
Our mind and body are strongly linked and our breathing rhythms show are emotional and mental condition. For instance, When a person encounters anxiety or stress, his breathing turns more rapid and shallow. However, during times of calmness, his breathing slows down and deepens. This mind-body link helps us to manage our emotions via conscious breathing.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is a kind of psychotherapy that investigates the connections between emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. This therapy concentrates on recognizing negative thought forms and beliefs to allow patients to acquire more practical options. It is a structured approach used for the treatment of a range of mental health issues.
The Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) techniques are the most widely practiced within psychology today. Therapists utilize CBT for better management of depression, anxiety substance use issues, eating disorders, and other mental health issues. CBT can provide multiple benefits when incorporated into therapeutic practices for psychological issues.
Following are some core principles of CBT:
CBT Principle |
Description |
Applications |
| Cognitive Distortions | Treats and questions negative thoughts and behaviors, replacing them with healthier ones. | It is helpful for general mental health improvements. |
| Thought-Behavior_Emotion Cycle | It focuses on the connection between emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. | It helps people better understand and manage their emotions. |
| Problem-Solving Focus | A goal-oriented and problem-focused approach to therapy. | This approach sets goals and resolves problems. |
| Behavioral Activation | It encourages people to be involved in meaningful activities to fight the feelings of depression. | Ideal for depression management. |
| Skills Development | This approach provides individuals with skills such as assertiveness, coping strategies, and relaxation techniques. | It enhances personal coping strategies. |
One proper technique that can enhance the effectiveness of CBT is conscious breathing. Conscious breathing practice or breathwork, are a range of breathing exercises intended to enhance physical, emotional and mental health. It refers to the practice of developing a soft awareness of one’s breath as it moves in and out of the body.
This practice can help someone achieve a state of calm, providing an excellent foundation for addressing negative thoughts and behaviours during therapy sessions. Following are common conscious breathing techniques:
Diaphragmatic breathing has been found to be particularly helpful in managing anxiety, making it a useful component of CBT.
An examination of conscious breathing and cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) reveals substantial evidence from clinical trials. These pieces of evidence support the positive effects these practices have on mental health practice. Specifically, they can provide psychological support and help alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, eating disorders and other mental health conditions such as bipolar disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
According to scientific studies, the breathing techniques have significant benefits in CBT. Scientific evidence also points to the psycho-physiological effects of breath control in CBT. They demonstrate that voluntary slowing down of breath frequency can lead to significant changes in brain-body interactions.
Although the exact mechanisms linking breath control to mental health are still under investigation. It’s clear that the practice holds a strong potential for improving one’s mental state.

Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and conscious breathing have also been shown to help us manage stress more effectively. One of the primary aims of CBT is to help individuals eliminate avoidant and safety-seeking behaviours and coping mechanisms. Such mechanisms prevent self-correction of faulty beliefs, thereby facilitating stress management and improving mental health.
An important aspect of stress reduction is teaching our minds and bodies to respond to emotional challenges more adaptively. CBT does so by encouraging us to challenge negative thought patterns and replace them with more helpful thoughts, ultimately promoting relaxation and calm.
On the other hand, conscious breathing exercises can be an essential part of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). This practice fosters awareness of our breath as it moves in and out of the body, helping us achieve a state of calm.
Several types of conscious breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing and alternate nostril breathing, can be integrated into our daily routines. Regular practice of these methods can boost our resilience to stress and anxiety.
Furthermore, studies have shown positive outcomes in using CBT and MBSR techniques to alleviate anxiety and depression in different populations, including autistic individuals.
A 2017 study found that both CBT and MBSR, which are therapeutic approaches that include mindful breathing, have helped reduce anxiety and depression among those on the autism spectrum.
Joining CBT with conscious breathing can complement each other in managing stress and anxiety. We can use cognitive restructuring and behavioural therapy strategies from CBT to change our thinking patterns. Whereas conscious breathing helps us stay present and grounded.
Incorporating CBT and conscious breathing into our lives can be an effective way to address stress, anxiety, burnout, and other distressing emotions. Through regular practice, we enhance our coping skills, our ability to navigate challenging situations, foster relaxation, and improve overall well-being.
When it comes to conscious breathing and managing stress, there are numerous techniques to choose from. In this section, we will discuss some practical breathing exercises that can help foster relaxation and mindfulness.
Belly breathing, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, is an effective technique for stress relief. To perform belly breathing, start by placing one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Breathe in deeply through your nose, allowing your belly to expand fully. Then, exhale slowly through your mouth. By focusing on the rise and fall of the abdomen, we can better connect with our breath and attain a more relaxed state.
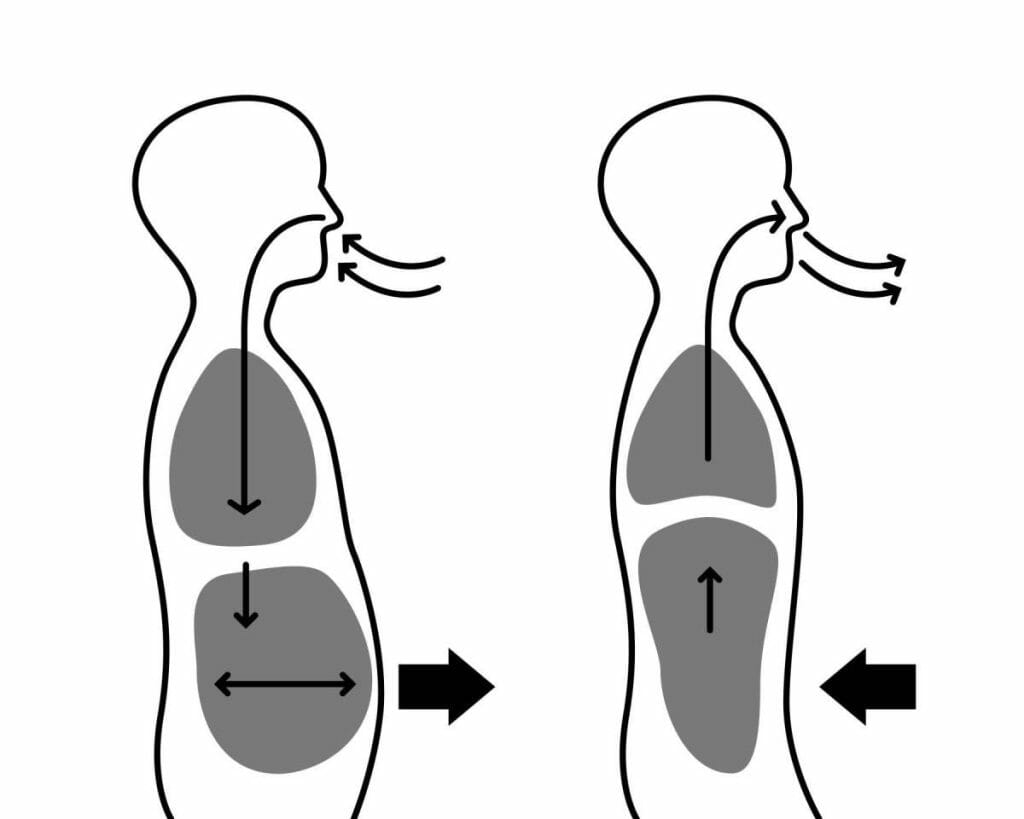
Box breathing, also called “square breathing“, is an easy yet powerful exercise mostly used in mindfulness practices and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy. It covers controlled, paced breathing in an organized pattern which relaxes the nervous system, lowers stress, and enhances focus. This breathing technique is known as “box breathing” because it aims for equal phases just like the sides of the square. It requires each phase _ to inhale, hold the breath, exhale, and then hold again, and is carried out for an equal count, generally about 4 seconds.
Alternative nostril breathing, also known as “Nadi Shodhana” is a yogic breathing exercise. It is frequently used in mindfulness-based CBT practices. In this technique, one breathes through one nostril while closing the other and then changing nostrils. The technique is perfect for stabilizing the mind and body, fostering relaxation, and wiping out mental fog. If you want to balance your autonomic nervous system to lower stress and anxiety, this technique is for you.
When you regularly do these practical cognitive Behavioural therapy exercises, they leave a significant impact on our overall well-being. Just dedicate a few minutes each day to conscious breathing. This will help you effectively manage stress and cultivate a greater sense of inner peace and balance.
Breathing Techniques |
Description |
Benefits |
| Diaphragmatic Breathing | Place one hand on your chest and the other on your belly. Inhale deeply through your nose, letting your belly expand. Exhale slowly through your mouth. | Reduces stress, and helps you feel more relaxed. |
| Box Breathing | Breathe in a controlled pattern: inhale, hold, exhale, hold, each for about 4 seconds. This creates a ‘box’ pattern with your breathing. | Calms the nervous system, and improves focus. |
| Alternate Nostril Breathing | Close one nostril, inhale through the other, then switch and exhale. Alternate each breath. Known as “Nadi Shodhana.” | Balances the mind, relieves stress, and clears mental fog. |
Incorporating conscious breathing techniques into our daily routines can have a profound impact on our physical health. We can experience improvements in several aspects of our health.
Following are some benefits of conscious breathing on our physical health.
Research shows that incorporating techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing can have a positive effect on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
Conscious breathing also has significant effects on the nervous system. By practicing controlled breathing techniques, we can positively influence our autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate and digestion.
The autonomic nervous system is composed of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. While the sympathetic nervous system activates the “fight or flight” response during stress or danger, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restorative functions.
When we practice conscious breathing, we engage the parasympathetic nervous system, which in turn activates our relaxation and calm states. Slow, deliberate breaths stimulate the vagus nerve, a crucial component of the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps to regulate heart rate, digestion, and other vital functions.
By focusing on our breath and the sensations it produces within our bodies, we can facilitate a shift from the “fight or flight” mode to a state of calm and relaxation. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals dealing with anxiety, stress, panic disorder or other related disorders.
Additionally, conscious breathing has a direct impact on the nervous system by promoting autonomic changes, such as increasing heart rate variability and respiratory sinus arrhythmia. It also modifies the central nervous system (CNS) activity leading to beneficial effects on brain function, such as increased alpha and decreased theta power in EEG studies.
Conscious Breathing Techniques in CBT can prove an effective and simple tool to reduce stress, foster relaxation, and support overall nervous system health and balance.
Breathing is a fundamental process of life. While it often happens unconsciously, there is a powerful connection between our breath and our overall well-being. Engaging in breathwork can help regulate our physical and mental states by striking a balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in our bodies.
The act of learning how to control our emotional state through conscious breathing is considered one of the most powerful psychological therapy tools available.
Conscious breathing involves developing a soft awareness of our breath as it moves in and out of our bodies. By controlling our breathing rate, we can achieve a state of calm and relaxation, which is beneficial for both our physical and mental health.
bobi, a personal breathing coach that helps users practice optimal breathing techniques. By using bobi, we can guide our breathwork practice, ensuring that we maintain a steady and comfortable breathing rate. This, in turn, helps us achieve a balance between our inhalation of oxygen and the exhalation of carbon dioxide, allowing our bodies to function efficiently.
Incorporating conscious breathing into our daily routines with the help of the bobi breathing companion improves our health and enhance our cognitive function and emotional regulation. As we take each breath, we deepen our focus and cultivate greater awareness, which can keep our minds clear and sharp.
Through a conscious breathing practice, we can achieve a sense of balance in both the body and mind. With the help of bobi, we can put these practices into action, taking control of our health and well-being one breath at a time.

Incorporating conscious breathing in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can provide significant benefits in managing both anxiety disorders and other mental health conditions. Through decades of experience and research, diaphragmatic breathing has been shown to be an effective technique for reducing anxiety and increasing emotional well-being.
One of the strengths of combining CBT with conscious breathing lies in the accessibility of these practices. Both techniques can be easily learned and implemented by individuals with bobi, regardless of their prior experience with mental health interventions. Additionally, they can be practiced in various contexts, whether in formal therapy sessions or during daily life.
In our clinical practice, we have also found that mindful breathing can enhance the efficacy of other CBT techniques. This is achieved by promoting greater self-awareness and emotional regulation. By becoming more attuned to our breath, we open up opportunities for deepening our understanding of our thoughts and feelings, which is a cornerstone of the CBT approach.
Moreover, the psychophysiological mechanisms underlying slow and mindful breathing are still being explored by researchers. However, existing studies have demonstrated strong correlations between these practices and improvements in overall mental health and well-being.
In short, the incorporation of conscious breathing into Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) provides a powerful tool to handle anxiety, stress, and a range of mental health issues. The focus of breathing exercises on mind-body connection, allows individuals to adjust their emotional reactions, lowers physiological stress, and enhances overall health. Conscious breathing not only helps in managing mental health disorders but also has deep effects on physical health, relaxing the nervous system and fostering a condition of balance.
Whether suffering from daily stressors or more serious issues such as PTSD and eating disorders, breathing exercises act as an available and efficient approach within CBT. Techniques such as box breathing, diaphragmatic breathing, and mindful breathing enable people to develop space between their responses and thoughts for more attentive reactions to life’s hurdles. But if you want to speed up the process and a beautiful journey toward improved mental and emotional health, then bobi is for you. Get your bobi from here!

CBT is a cognitive therapy, that helps individuals address negative thoughts and behaviours by challenging and replacing them, leading to healthier behaviour patterns.
Conscious breathing promotes relaxation and mindfulness, making individuals more present and grounded. This enhances the effectiveness of CBT by providing a calm foundation for addressing negative thoughts and behaviours.
CCB is a type of conscious breathing that uses connected, full breaths combined with body-mind techniques to support physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual well-being.
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as deep breathing, involves pulling the diaphragm down while taking a deep breath in. It has been found to be particularly helpful in managing anxiety.
Both practices can alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions. They help regulate emotional responses, reduce stress, and improve overall, mental health professional well-being.
CBT helps individuals challenge negative thought patterns, while conscious breathing exercises foster relaxation and mindfulness. Together, they enhance resilience to stress and anxiety.
Techniques like belly breathing and the 4-7-8 breathing method can foster relaxation and mindfulness.
It can improve exercise performance, heart rate, blood pressure, and overall a better quality of of life. Regular practice can also reduce stress and anxiety levels, leading to better emotional and stress management too.
Conscious breathing engages the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and restorative functions. It can reduce stress, foster relaxation, and support overall nervous system health.
bobi is a breathing companion that guides users in practicing optimal breathing techniques, helping maintain a steady breathing rate and balance between oxygen intake and carbon dioxide exhalation.
Combining CBT with conscious breathing provides an accessible and effective tool, for individuals seeking growth and emotional resilience. It promotes self-awareness, emotional regulation, and overall mental health improvement.
Diaphragmatic breathing in CBT means deep breathing from the diaphragm instead of surface chest breathing, which helps soothe the nervous system and decreases stress. This exercise fosters relaxation, controls anxiety, and boosts concentration through therapy sessions.
Breathing exercises activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps reduce anxiety by lowering the body’s fight or flight response and fostering relaxation.
Some powerful breathing techniques used in CBT are Diaphragmatic Breathing, Box Breathing, and Alternate Nostril breathing.
Stay updated on what's happening at bobi, and all things breathing, anxiety and mental wellness.